Cephalanthus Occidentalis FAQs
As someone who’s spent quite a bit of time with the Cephalanthus Occidentalis, or commonly known as Buttonbush, I’ve gathered some insights and answers to frequently asked questions about this fascinating plant. Whether you’re new to growing it or simply curious, here’s a comprehensive guide to help you understand more about Cephalanthus Occidentalis.
What is Cephalanthus Occidentalis?
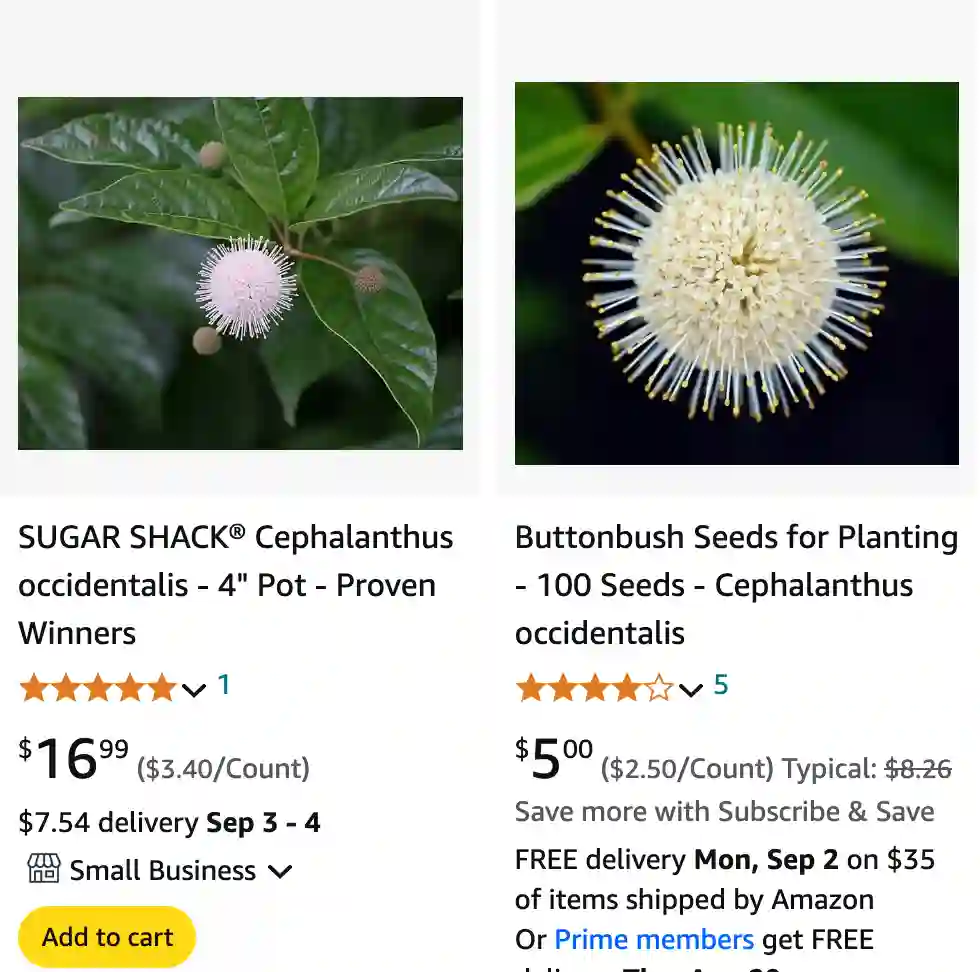
Cephalanthus Occidentalis, also known as Buttonbush, belong to the Rubiaceae family, is a deciduous shrub native to North America. It is well-regarded for its unique, spherical flower clusters that resemble buttons. These flowers are a striking feature in any landscape, and they often attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Plant Family: 616 Genera in Rubiaceae – Coffee Family
Are the Flowers on Cephalanthus Occidentalis Also Seed Pods?
No, the flowers on Cephalanthus Occidentalis are not seed pods. The plant produces small, white to creamy flowers that cluster together to form a globe-like shape. These flowers are quite ornamental and give way to the seed pods after blooming. The seed pods develop later in the season and are a different structure altogether from the flowers.
How Can Cephalanthus Occidentalis Be Reproduced?
Cephalanthus Occidentalis can be reproduced in a couple of ways:
- Seeds: The most common method is through seeds. After the flowering period, the plant produces seed pods which, when mature, can be harvested and sown.
- Cuttings: Another effective method is to propagate through cuttings. Semi-hardwood cuttings taken from the plant during the summer can be rooted in a well-draining soil mixture.
How Does Cephalanthus Occidentalis Survive?
Cephalanthus Occidentalis is quite resilient. It thrives in wet to moist conditions, often found in swamps or along riverbanks. It can handle a range of soil types, including clay and sandy soils, as long as they are well-drained. This plant is also known for its ability to tolerate flooding, making it a good choice for wetter garden areas.
How to Germinate Cephalanthus Occidentalis Seeds?
Germinating Cephalanthus Occidentalis seeds involves a few steps:
- Stratification: Before sowing, the seeds need to be stratified. This means placing them in a refrigerator for about 30 days to simulate winter conditions. This process helps break the seed’s dormancy.
- Sowing: After stratification, sow the seeds in a seed tray or pots filled with a moist, well-draining soil mix. Press them gently into the soil but don’t cover them completely.
- Conditions: Keep the seeds in a warm, bright location. Maintain consistent moisture and be patient, as germination can take several weeks.
Is Cephalanthus Occidentalis Edible?
Cephalanthus Occidentalis is not typically considered edible. While there’s no widespread use of the plant in culinary applications, it is not known to be toxic either. The plant is mainly grown for ornamental purposes and its ecological benefits rather than for consumption.
How to Care for Cephalanthus Occidentalis?
Caring for Cephalanthus Occidentalis is relatively straightforward:
- Watering: Ensure the plant has access to plenty of water, especially in its growing season. Regular watering is crucial, particularly in dry spells.
- Pruning: Prune the plant in late winter or early spring to maintain its shape and remove any dead or damaged branches.
- Fertilizing: Fertilize with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring to promote healthy growth and flowering.
What to Plant With Cephalanthus Occidentalis?
Buttonbush pairs well with other moisture-loving plants. Consider companion plants like:
- Swamp Milkweed (Asclepias incarnata): Attracts pollinators and complements the buttonbush’s wetland habitat.
- Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis): Adds vibrant color and thrives in similar conditions.
- Japanese Iris (Iris ensata): Provides visual interest and enjoys the same moist soil conditions.
Can You Grow Cephalanthus Occidentalis Indoors?
While Cephalanthus Occidentalis is typically grown outdoors, it can be grown indoors if you can provide the right conditions. It needs ample sunlight and high humidity, which can be challenging to maintain indoors. However, with the right setup, such as a large, bright window or grow lights and a humidifier, it can be a unique indoor plant.
Is Cephalanthus Occidentalis Toxic?
Cephalanthus Occidentalis is not considered toxic to humans or pets. It is safe to grow in gardens with children and animals. However, as with any plant, it’s always wise to prevent ingestion of plant material.
Common Problems with Cephalanthus Occidentalis
- Pests: Watch out for common pests like aphids and scale insects. Regular inspections and appropriate treatments can help manage these issues.
- Diseases: The plant can occasionally suffer from fungal infections, especially in overly damp conditions. Ensure good air circulation and avoid overhead watering to reduce disease risks.
Compare with Other Similar Plants
Compared to other wetland plants like Syringa (Lilac) or Acer (Maple), Cephalanthus Occidentalis stands out for its distinctive flower structure and wetland adaptability. Unlike the more common Lilac, which prefers drier conditions, Buttonbush excels in soggy soil, making it a versatile choice for a variety of garden settings.
With these insights, I hope you have a clearer understanding of Cephalanthus Occidentalis. Whether you’re considering adding it to your garden or just learning more about it, this plant’s unique characteristics make it a fascinating addition to any landscape.
If i die, water my plants!



