657 Species in Genus Quercus – Oak Tree
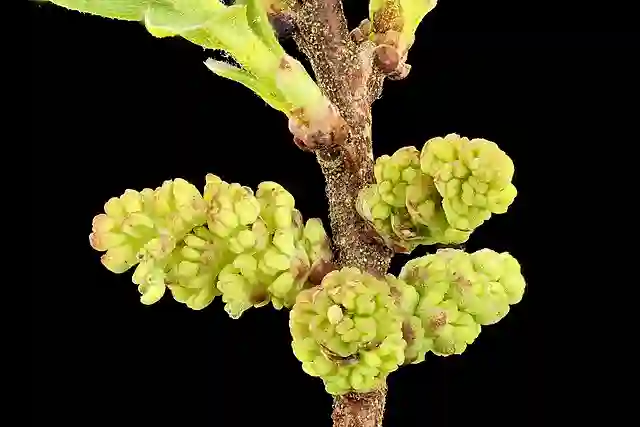
What is Quercus Bicolor?
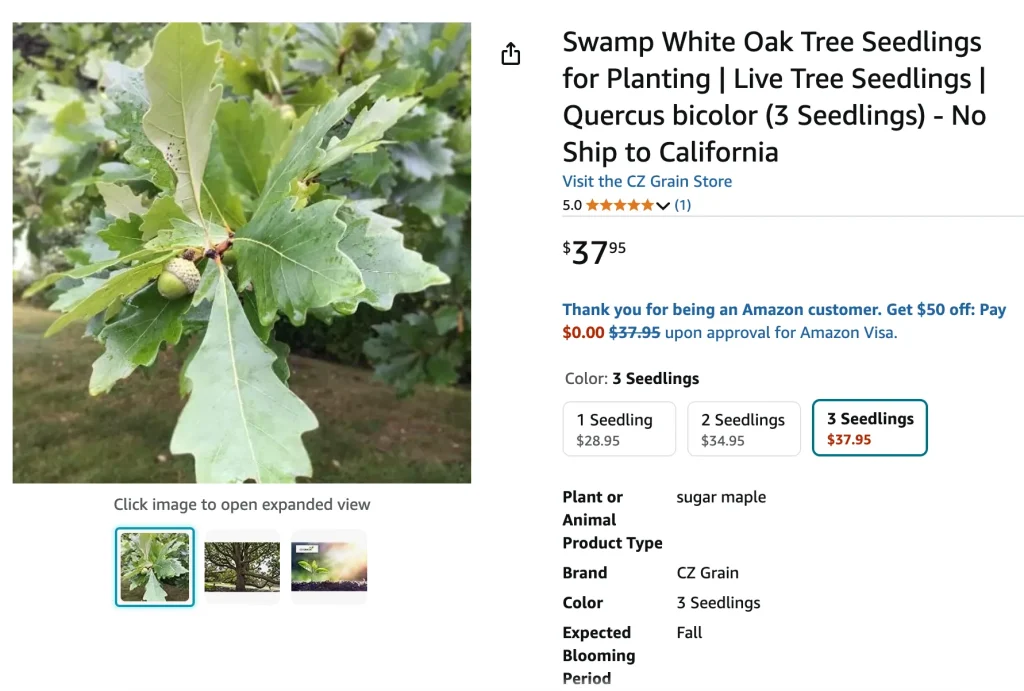
Quercus bicolor, commonly known as the Swamp White Oak, is a medium to large deciduous tree native to North America. It is well-loved for its beautiful, lobed leaves that are green on top and silvery-white underneath. This tree thrives in wet or swampy conditions, hence its name, but it’s also highly adaptable to various soil types. It is a long-lived tree, often growing to heights of 50-80 feet with a wide-spreading canopy, making it a popular choice for shade in landscapes.
How to care for Quercus Bicolor?
Caring for Quercus bicolor is relatively simple. Plant it in a location with full sun to partial shade, and ensure the soil is well-drained or occasionally moist. While it’s highly tolerant of wet conditions, it can also adapt to drier soils once established. Regular watering during the first few years helps the tree develop a deep root system. Prune only to remove dead or damaged branches, preferably in late winter or early spring. Fertilization is rarely necessary unless the soil is particularly nutrient-deficient.
How to propagate Quercus Bicolor?
The most common method of propagating Quercus bicolor is through its acorns. Collect ripe acorns in the fall, remove any with holes or damage, and store them in a cool, moist place until spring. Before planting, soak the acorns in water for 24 hours to encourage germination. Plant them about 1-2 inches deep in a pot or directly in the ground. Keep the soil moist but not soggy, and be patient, as germination can take several weeks.
What to plant with Quercus Bicolor?
When planting Quercus bicolor, consider pairing it with native understory plants like serviceberry (Amelanchier), redbud (Cercis), or spicebush (Lindera benzoin). Groundcovers like ferns, wild ginger (Asarum canadense), or native grasses such as sedges (Carex species) also work well. These companions not only complement the tree visually but also help create a biodiverse and sustainable habitat.
Can you grow Quercus Bicolor indoors?
No, Quercus bicolor is not suitable for growing indoors. It is a large, outdoor tree that requires ample space, sunlight, and natural soil conditions to thrive. While you can start acorns in pots indoors for propagation purposes, the tree itself needs to be transplanted outside once it outgrows its container.
Is Quercus Bicolor toxic?
Quercus bicolor is not considered highly toxic, but its acorns contain tannins, which can be harmful if consumed in large quantities by humans or animals like dogs and livestock. While occasional ingestion of acorns is unlikely to cause significant harm, it’s best to keep them out of reach of pets and children.
What are the benefits of Quercus Bicolor?
Quercus bicolor offers numerous benefits. Its dense canopy provides excellent shade, making it a great addition to parks and large gardens. Ecologically, it supports a variety of wildlife, including birds, squirrels, and insects. The tree’s acorns are a valuable food source for many animals. Additionally, it’s a hardy and low-maintenance tree that can tolerate urban conditions, such as pollution and compacted soil.
What are common problems with Quercus Bicolor?
Common issues with Quercus bicolor include leaf spot diseases, powdery mildew, and oak wilt. Pests such as borers and caterpillars may also occasionally pose problems. To prevent these, ensure the tree is planted in the right conditions and receives adequate care. Avoid injuring the bark, as this can make the tree more susceptible to diseases and pests.
How does Quercus Bicolor compare with other oak species?
Quercus bicolor is often compared to Quercus alba (White Oak) due to their similar appearance. However, the Swamp White Oak is more tolerant of wet conditions, making it a better choice for poorly drained areas. Its leaves have a distinctive silvery underside, which is a key differentiator. Compared to Red Oaks (Quercus rubra), it’s less prone to oak wilt and adapts better to wetter soils.
Can Quercus Bicolor tolerate urban environments?
Yes, Quercus bicolor is highly adaptable to urban settings. It can tolerate pollution, compacted soil, and occasional droughts, making it an excellent choice for city parks, street plantings, and large residential landscapes.
What makes Quercus Bicolor unique?
One unique feature of Quercus bicolor is its ability to thrive in wet, swampy areas where many other trees struggle. Its striking leaves with silvery undersides also set it apart visually, adding a subtle shimmer in the wind. Additionally, its acorns have a relatively short maturation period of just one growing season, unlike some other oak species that take two years.
Is Quercus Bicolor a fast-growing tree?
Quercus bicolor grows at a moderate rate, typically adding 12-24 inches in height per year under optimal conditions. While it’s not the fastest-growing tree, its long lifespan and sturdy structure make it well worth the wait.
If i die, water my plants!



