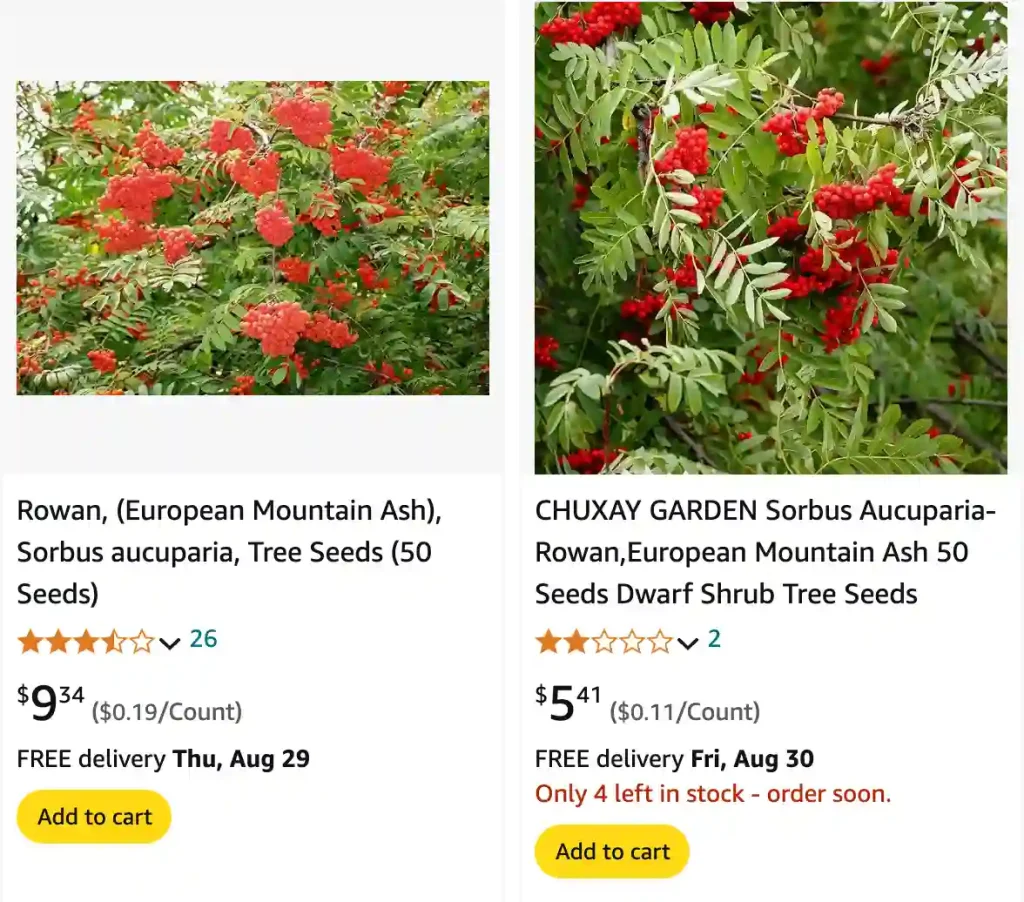
What is a Rowan Tree?
A Rowan Tree, also known as the Sorbus Aucuparia, is a small to medium-sized tree that belongs to the Rosaceae family. It’s often referred to as the Mountain Ash, though it’s not a true ash tree. Rowan trees are celebrated for their beautiful clusters of white or pink flowers in spring, their vibrant red or orange berries in autumn, and their strikingly colorful foliage that turns shades of yellow and red as the seasons change. These trees have been cherished in various cultures for centuries, often associated with folklore and protection.
107 Species in Genus Sorbus
Where Do Rowan Trees Grow?
Rowan trees are native to Europe and parts of Asia. They thrive in temperate climates and are commonly found in woodlands, on hillsides, and in rocky soils. They can adapt to a range of soil types, though they prefer well-drained, slightly acidic to neutral soils. In the United States, Rowan trees are less common but can be grown in certain regions that match their native conditions, especially in cooler climates.
Can You Eat Rowan Tree Berries?
Rowan tree berries are edible, but they are not commonly eaten raw due to their bitter taste and astringency. When consumed raw, they can cause stomach upset. However, they can be made palatable through cooking. Rowan berries are often used to make jellies, jams, and even liqueurs. They are high in vitamin C and can be a nutritious addition when prepared properly. Always ensure that the berries are fully ripe before use, as unripe berries can be particularly harsh.
Are Mountain Ash and Rowan Trees the Same?
Yes, Mountain Ash is a common name for the Rowan Tree. Despite their common name, Rowan trees are not true ash trees but belong to the Sorbus genus. The term “Mountain Ash” is used due to their similar leaf shape and growth habit to true ash trees, but biologically, they are quite different.
Are Rowan Tree Berries Poisonous to Dogs?
Rowan tree berries are not highly toxic to dogs, but they can cause gastrointestinal upset if consumed in large quantities. The berries contain compounds that can irritate the digestive system. If your dog eats a small number of berries, they might experience mild symptoms such as vomiting or diarrhea. However, if a significant amount is ingested or if symptoms persist, it’s best to consult a veterinarian.
Are Rowan Tree Roots Invasive?
Rowan tree roots are generally not considered invasive. They are relatively non-aggressive compared to some other species. Rowan trees have a fibrous root system that doesn’t typically spread aggressively or cause damage to nearby structures. They can be a good choice for garden spaces where a less invasive root system is desired.
Can I Grow a Rowan Tree in a Pot?
Yes, you can grow a Rowan tree in a pot, especially if you have limited space or want to keep the tree small. Choose a large pot with good drainage and use a high-quality potting mix. Regular watering and fertilizing will help the tree thrive in its container. Be prepared for the tree to need repotting as it grows, and ensure it receives sufficient sunlight.
Can You Keep a Rowan Tree Small?
While Rowan trees are naturally small to medium-sized, you can control their size through regular pruning. By cutting back the tree’s growth each year, you can maintain a more compact size and shape. This is particularly useful for growing Rowan trees in smaller gardens or pots where space is limited.
How Fast Do Rowan Trees Grow?
Rowan trees are relatively slow to moderate growers. They typically grow around 12 to 24 inches per year, depending on the growing conditions. Factors such as soil quality, sunlight, and water availability can affect their growth rate. In optimal conditions, you might see faster growth, but generally, patience is required as these trees develop.
How Long Do Rowan Trees Live?
Rowan trees have a relatively long lifespan. In their native environments, they can live for several decades, often reaching up to 50 years or more. Their longevity can be influenced by factors such as climate, soil conditions, and care. With proper attention and suitable growing conditions, a Rowan tree can be a lasting and beautiful addition to your landscape.
Rowan Tree vs. Mountain Ash
As previously mentioned, Rowan trees and Mountain Ash refer to the same species, Sorbus aucuparia. The name “Mountain Ash” is used due to the tree’s similar appearance to ash trees, though it is not related to the true ash species. Both names are used interchangeably depending on regional preferences.
How to Care for a Rowan Tree
Caring for a Rowan tree involves regular watering, especially during dry spells, and ensuring it has well-drained soil. Pruning helps maintain its shape and encourages healthy growth. Rowan trees are generally hardy but may benefit from mulching to protect the roots and conserve moisture. Watch for pests and diseases, and address any issues promptly to keep your tree healthy.
How to Propagate a Rowan Tree
Rowan trees can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. For seed propagation, collect and stratify the seeds before sowing them in a cold frame or nursery bed. For cuttings, take semi-hardwood cuttings in late summer and root them in a moist, well-draining medium. Both methods require patience, but they can successfully produce new Rowan trees.
What to Plant With Rowan Trees
Rowan trees work well in mixed borders with other shrubs and perennials that enjoy similar soil and light conditions. Companion plants might include other native shrubs, ornamental grasses, or shade-tolerant perennials. Avoid planting them near invasive species or plants that compete heavily for nutrients and water.
Is It Toxic?
Rowan trees are not highly toxic, but caution is advised with the berries, especially around pets and young children. Proper preparation of the berries can make them safe for human consumption, but they should not be eaten raw in large quantities.
Benefits of Rowan Trees
Rowan trees offer several benefits, including their ornamental value with stunning seasonal displays. They attract wildlife, such as birds, that feed on the berries. Rowan trees also contribute to biodiversity and can be used in various traditional remedies and crafts.
Common Problems with Rowan Trees
Common issues with Rowan trees include fungal diseases like leaf spot and rust, as well as pests such as aphids and scale insects. Regular inspection and prompt treatment can help manage these problems and keep your Rowan tree healthy.
By understanding these aspects of Rowan trees, you can better appreciate their unique qualities and care for them effectively, ensuring they remain a vibrant part of your landscape for years to come.
If i die, water my plants!



